The tragedy of the Commons
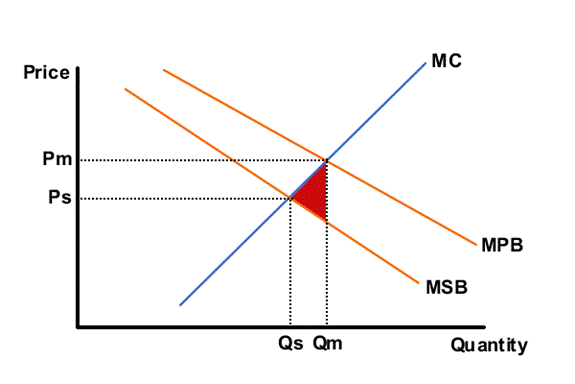
The overgrazing cost shown in Hardin's analogy is an example of a negative externality of consumption, where the private utility is diminished by the negative utility suffered by third parties; in this case the other herders. The grazing land is over-consumed and so there is a welfare loss.
To reduce these negative externalities, Hardin suggests potential management solutions for common goods including privatisation, environmental taxation, government regulation and stricter management by the state. The nature of this regulation depends on whether the resources are within national boundaries or global in nature. Where national resources are concerned; rules on their use can be imposed by national governments. Global common access resources, such as fishing grounds, will require the creation of international regulatory organisations to control their use. Hardin also suggests the transfer of common access resources to private ownership. In keeping with his original pasture analogy, he categorises this as the enclosure of the commons.
The 'Tragedy of the Commons' is an analogy. The major theme running through Hardin's work is, in fact, the growth of human populations with the Earth's resources being a general 'common'. He focuses on the allocation and exploitation of larger resources, such as the Earth's atmosphere and oceans, and the 'negative commons' of pollution.
Garrett Hardin on the Tragedy of the Commons and Resources
In this video, Garrett Hardin is interviewed on the Tragedy of the Commons and Resource Allocation: As Hardin says:

The Tragedy of the Commons is concerned with the allocation of resources...The unmanaged commons cannot possibly work once the population gets about a certain size.
