Qualitative forecasting/data

When no hard (numeric) data is available, qualitative data may be needed to predict future events or behaviour. This data relates to judgements and opinions. Two possible methods are:
-
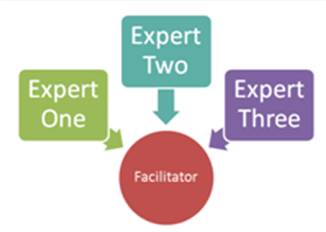 The Delphi Technique - Here a panel of experts is interrogated through a sequence of questionnaires, each of which builds on previous questionnaires in a series of 'rounds'. The experts answer independently of each other. After each round, a facilitator provides an anonymous summary of the experts' forecasts from the previous round as well as the reasons they provided for their judgments. The experts are encouraged to revise their earlier answers in light of the replies of other members of their panel. It is believed that the group will eventually reach a consensus. The process is stopped after a number of rounds or when a consensus is reached.
The Delphi Technique - Here a panel of experts is interrogated through a sequence of questionnaires, each of which builds on previous questionnaires in a series of 'rounds'. The experts answer independently of each other. After each round, a facilitator provides an anonymous summary of the experts' forecasts from the previous round as well as the reasons they provided for their judgments. The experts are encouraged to revise their earlier answers in light of the replies of other members of their panel. It is believed that the group will eventually reach a consensus. The process is stopped after a number of rounds or when a consensus is reached.
- Panel Consensus - Here experts work co-operatively to suggest answers.
