Position/perception maps
One marketing research technique is taking consumer's views about a product and then plotting (mapping) these perceptions on a positioning chart. Respondents are asked questions about their experience with the product or service in terms of its performance, packaging, price and size. These qualitative answers are transferred to a chart referred to a position or perception map. The results can be used to improve the product or provide the background for developing new ones.
This position map defines the market in terms of the way buyers perceive key characteristics of competing products. The basic position map normally uses price and quality as the two key variables, but other variables are used, such as low or high calorie if mapping food items, or size related to cars.
Figure 1 Product positioning map
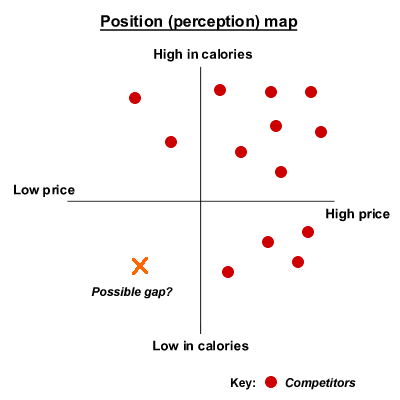
Figure 2 Product positioning map - example
The firm may map its proposed market to find a 'gap' in the market, where a new product may be positioned and the firm may seek growth. If the position map displays a cluster in one part of the market then the firm may avoid that area because of the high density of competition.
In the example above, high-priced, high calorie products are produced by a number of firms. These might be the 'indulgence' product such as rich ice-creams or confectionary. It may be very difficult to enter this segment unless the firm has a very strong brand image that matches the product requirements. However, there is a gap in the market for a product that is both low in calories and low in price. The firm must consider whether it has the strengths or assets to take advantage of this gap and whether the gap exists, because it may not be profitable to produce such a product.
The positioning map also reflects what your customers think about your brand. This may not be quite what you had in mind. Skoda, for instance, after it was bought by VW, spent millions on its marketing in an attempt to reposition itself in the minds of customers who had spent many a happy hour making up jokes about the poor quality of its cars. It was a difficult task, but one which has been accomplished successfully. Corporate image now matches product quality and price.
Think for a second about developments that are taking place in music. How can the music industry react to recent trends and position themselves in the market? Once you have had a think about this follow the Music link.

Group discussion
Using your knowledge of the music and entertainment scene and also technology developments, vision forward five years and produce a top ten of developments in the entertainment industry.
Once you have completed this exercise, examine the consequences for existing media corporations of these developments and for the marketing and distribution of new music and film.