Profit - notes
Within economics you will meet:

- Normal profit - is that level of profit which is just sufficient to keep the firm in its present use. Normal profit is assumed to be an element of the ATC curve.
- Supernormal profit (or abnormal profit)- this is any profit made in excess of normal profit.
The definitions of supernormal and normal profit mean that profit on a diagram drawn by an economist shows supernormal profit only. Normal profit is included as an element of the ATC curve and arises where ATC = AR. Examine the following diagrams (we'll look at how to build these diagrams in more detail later on):
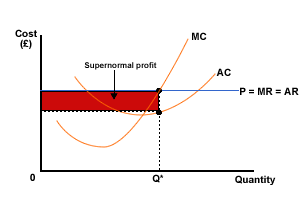
Figure 3 Firm in perfect competition - supernormal profit
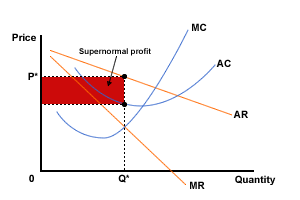
Figure 4 Monopoly - supernormal profit
This has to be compared with the accountant's definition of profit.
Accounting profit
The difference between revenue from sales and the costs incurred in making these sales, regardless of any credits given or taken.
Accountants deal in facts. They do not get involved with concepts such as normal profit. Governments tax accounting profit, not normal profit.
Why do firms try to make a profit?
Profit has many uses:
- It is the return to the entrepreneur.
- It is a source of funds for development
- It is a motivator.
Profit is a driving force within business. It is an incentive for investors to invest. It lies behind all cost reduction exercises, as the aim of cost reduction is profit maximisation.
