Trade problems (LDCs)
Syllabus:Trade problems facing many economically less developed countries
With reference to specific examples (Data Response remember), explain how the following factors are barriers to development for economically less developed countries:
- Over-specialization on a narrow range of products
- Price volatility of primary products
- Inability to access international markets
With reference to specific examples, evaluate the following factor as a barrier to development for economically less developed countries.
- Long-term changes in the terms of trade
-
Overspecialization on a narrow range of products (Plus Page 99)
Developing economies mainly trade in primary (Commodities) exports.
The export revenue earned from their sale pays for imports of manufactured goods. Diversification has been a slow process and it has a strong geographic bias. The Far Eastern economies have been able to move up through the categories of exports to command increased market shares of low and medium technology goods. Alas, for many of the poorer African countries, the reliance on low-valued primary exports has not fallen by a significant amount in their sources of foreign exchange earnings.
In 1970, primary exports constituted 72% of total developing country exports. By 1999, this had fallen to 48% for low-income countries and 32% for middle-income countries. Nevertheless, this proportion still contrasts noticeably with only 18% for advanced economies. The percentage remains exceptionally high for many of the poorest African countries at over 90%.

What the data shows
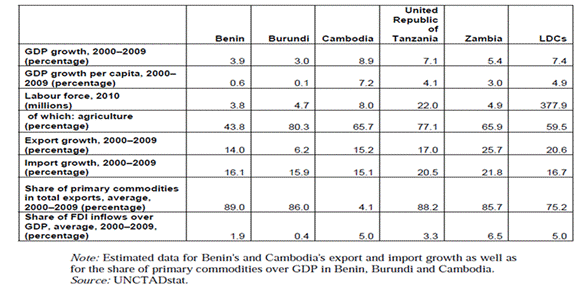
Examine the data above. What conclusions can you draw about the reliance of less developed countries on primary commodities?