4.1 Economic development - What is an LDC?
In this section we will look at the nature of economic growth and economic development.
Syllabus: Common characteristics of economically less developed countries
Explain, using examples, that economically less developed countries share certain common characteristics(noting that it is dangerous to generalize as there are many exceptions in each case), including
- low levels of GDP per capita,
- high levels of poverty,
- relatively large agricultural sectors,
- large urban informal sectors and
- high birth rates.
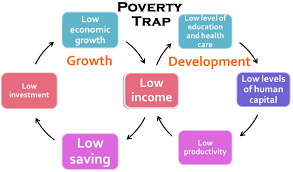
communities are unable to invest in physical, human and natural capital due to low or no savings; poverty is
therefore transmitted from generation to generation, and there is a need for (Government and/or NGO and /or Private Sector) intervention to break out of the cycle.
Syllabus: Diversity among economically less developed nations
Explain, using examples, that economically less developed countries differ enormously from each other in terms of avariety of factors, including:
- resource endowments,
- climate,
- history (colonial or otherwise),
- political systems and
- degree of political stability.