AD/AS - self-test questions

1 |
Shifts in aggregate demandWhich of the following would NOT cause a shift in AD? |
2 |
3 |
Shifts in aggregate supplyWhich of the following would NOT cause a SHIFT in AS? |
4 |
Shifts in aggregate supplyIf the price of imports rose, caused by a change in the value of the pound then the AS would shift to the: |
5 |
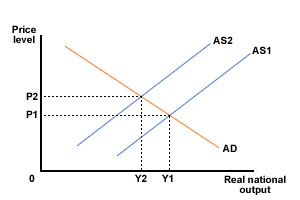
Shifts in aggregate supply
Which of the following might have caused the shift in aggregate supply shown in the diagram below? Tick all the answers that apply.
|
6 |
Determinants of exportsA key determinant of exports is: |
7 |
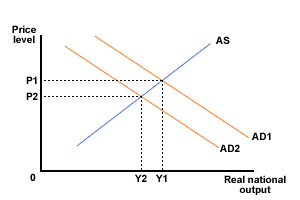
Shifts in aggregate supply and demand
Which of the following would cause the shift shown in the diagram below? Tick all the answers that apply.
|
8 |
AD/AS analysisWhen using AD/AS analysis to illustrate changes within an economy, which of the following would NOT need to be considered when looking at changes to economic growth? |
9 |
Aggregate supplyWhich of the following is a major influence on AS? |
10 |
11 |
Shifts in aggregate supply and demandAn increase in aggregate demand (given no change in aggregate supply) will cause higher inflation. |
12 |
Shifts in aggregate supply and demandAn increase in costs will make the aggregate supply curve more inelastic. |
13 |
Shifts in aggregate supply and demandThe less responsive is AS to a rise in AD, the more prices will rise for a given increase in AD. |
14 |
Shifts in aggregate supply and demandAn increase in expenditure tax will shift both the aggregate demand and supply curves to the left. |
15 |
Shifts in aggregate supply and demandAn improvement in productivity will shift both the aggregate demand and supply curves to the right. |
16 |
Increase in ADWhich of the following is likely to result from a rapid rise in aggregate demand? |