Syllabus: With reference to specific examples, evaluate each of the following as a means of achieving economic growth and economic development.
(e) Bilateral and regional preferential trade agreements
Prior to reading this section, you are advised to review Section 3.4 on Economic Integration
The principle of comparative advantages explains the potential gains to trading partners from freeing up trade by removing barriers, such as tariffs and other forms of protectionism. A liberalisation strategy to trade results in countries engaging in different degrees of economic cooperation and integration.
Economic integration
Economic integration refers to trade unification between different states by the partial or full abolishing of customs tariffs on trade taking place within the borders of each state.
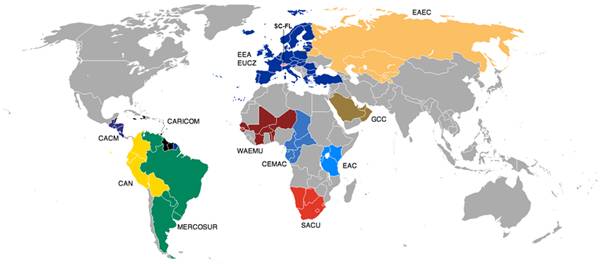
World Customs Unions
Economic integration can take a number of different forms including establishing a preferential trading area, free trade area, monetary union, customs union, common market, economic union, customs and monetary union and economic and monetary union (review Syllabus area 3.4 International Economies)
This section focuses on how less developed countries attempt to stimulate trade and benefit from economic integration. Many less developed countries have set up preferential trade agreements in an attempt to free up trade between participating members.
Preferential trade agreements can be either bilateral or regional:
- Bilateral trade agreements exist where two countries establish a preferential trade agreement between themselves.
- A regional trade agreement is a multilateral arrangement that exists between a number of countries in a geographical region. Regional trade agreement are sometimes referred to as 'trading blocs'. These provide for preferential access to certain products from participating countries by reducing (although not abolishing) tariffs. The establishments of regional trade agreements are often the first stage of economic integration prior to becoming a free trade area.
Preferential trade agreements have created numerous departures from the most favoured trading nation (MFN) principle of the World Trade Organization, where members are expected to apply the same tariffs to imports from other WTO members.
Note the command word EVALUATE in the syllabus statement so a Data Response Question could be about this:
For example:
Nov 2012
Q5d Using information from the text/data and your knowledge of economics, evaluate the likely effects of Malawi’s trade and development agreement with the EU. [8 Marks]
Example 2:
Nov 201Q4d Using information from the text/data and your knowledge of economics, evaluate the consequences of the Thailand-China free trade agreement (FTA) on Thailand’s growth and development.