Private and Public sector

Private Sector Business
Definition: Organisations owned, controlled and managed by private individuals, usually for the purpose of making profit.
Public Sector Organisations
Definition: The public sector is the government sector of the economy - orgnisations owned and run by the governmentPublic ownership is much
less common these days as it is believed that businesses are much more
efficient if they are privately owned. In the past few decades (since
the start of the 1980s) many businesses around the world have been
privatised. This means that they have been changed from public
ownership to private ownership.
However, the balance between public and private ownership varies considerably from country to country. In recent years, several governments have begun to create partnerships with the private sector (Think: Petrobras) and there is much more of what is called state capitalism
Infrastructure is another major area of plublic and private partnerships (Think: Toll Roads out of Sao Paulo)
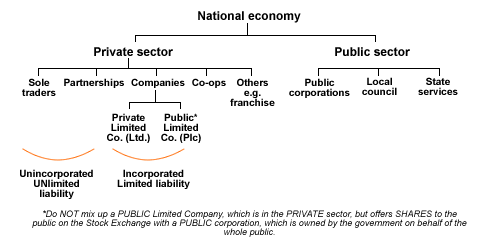
Overview of types of Organisation
SUMMARY of types of organisations in the private and public sectors
 Privatisation
Privatisation
Privatisation is the selling of nationalised or state-owned industries to private investors, moving the organisation from the public to the private sector.
Benefits of privatisation:
- Reduces costs - the profit motive, and competitive pressures will drive costs down. Often a state regulator ensures that private firms do not exploit their monopoly position in the market.
- Increases choice
- Increases quality
- Encourages innovation and invention
- Brings market forces into play in a positive manner for the consumer
- Saves the government money - the costs of the nationalised industries would be replaced by income from business taxes
- Widens share ownership in the population
Problems of Privatisation:
- Monopolies will be in private hands and need regulating e.g. Nuclear industry, transport
- Loss of income for the government - the general public loses a valuable resource
-
Externalities - a private firm may not be so careful about environmental issues
Privatisation in many countries has been accompanied by the introduction of deregulation to promote competition and efficiency
 Deregulation
Deregulation
Deregulation is the removal of government rules, controls and restrictions on production and trade.
