Promoting Clean Technologies

Clean technologies
Clean technologies are designed to minimise pollution and the emissions of greenhouse gasses, by creating electricity and fuels with a smaller environmental and carbon footprint. These technologies include recycling, renewable energies (wind and solar power, biomass and biofuels and hydropower), green transportation, waste water recycling and energy efficient lighting, homes, buildings, electric motors and commercial and domestic appliances.
The World Bank is the trustee of the Clean Technology Fund (CTF), focused on making renewable energy cost-competitive with coal-fired power. Since its launch in 2008, $US6.5 billion has been allocated to climate change projects in 45 developing countries. These payments represent a subsidy on the development and use of clean technologies.
If government or World Bank subsidies are particularly focused on the generation of electricity using renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, then firms generating electricity using cleaner technologies will face lower costs of production. This will encourage energy producers to produce more wind and solar power, shifting the supply curve to the right and lowering prices for consumers.
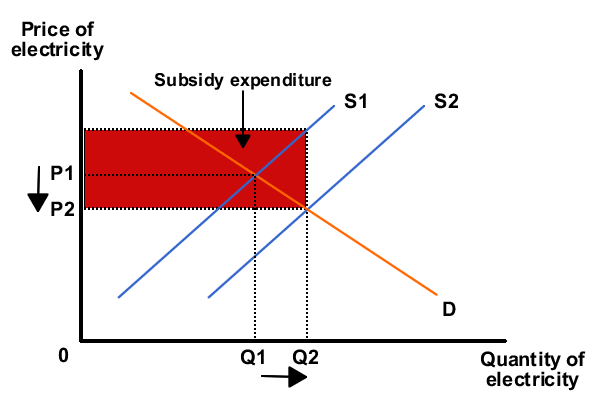
Subsidies or tax credits should also encourage increased investment in clean technologies. However, UN research showed 'green' investment in Europe dropped by one-fifth in 2010, while that in developing countries surge ahead.

Read the following articles and then produce a 750 word report comparing and contrasting Europe's commitment to renewable energies and cleaner technologies to that of some developing countries. Use appropriate data to support your analysis.
