Price floors
If you would prefer to view this interaction in a new web window, then please follow the link below:
Minimum wage
Many countries have now set a minimum wage. A minimum wage was first enacted in New Zealand in 1894 and there is now legislation setting minimum wages in more than 90% of all countries. The effect of a minimum wage will be very similar to that of a minimum price.
Assuming that the minimum wage is above the equilibrium level, wages will rise to the minimum wage level, but the number of employees will fall (to Qd in Figure 2), at least in the short run.
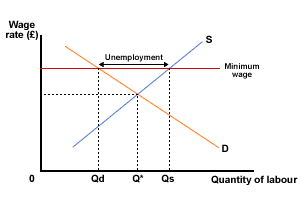
Figure 2 Impact of a minimum wage
However, the extent of the unemployment will depend on the elasticity of demand for and elasticity of supply of labour. If both are very inelastic then there may be very little unemployment. Don't worry, this will be more fully explained later!
If the substitutability of labour is very low (in other words employers cannot substitute capital (machines) for labour), then this should help minimise the impact on unemployment.
However, unscrupulous employers may well employ workers illegally and pay less than the minimum wage. An informal market is again created. This is often found where countries have a large number of illegal immigrants.

Task
Use the web to find out if there is a minimum wage in your country. If there is, try to answer the following questions.
- What is the level of the minimum wage?
- What age does it start at?
- Are there any exceptions where employers are allowed to pay below the minimum wage?
- How much has it increased in real terms (compared to inflation) in the last five years?
